This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more
This test allows evaluation of working memory. When placed in the Y-maze, mice tend to alternate visits between the three arms. A mouse with impaired working memory cannot remember which arm it just visited and thus shows decreased spontaneous alternation.
Home-made equipment made of PVC.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
This is an associative learning paradigm for measuring emotional learning and memory. A neutral conditioned stimulus (CS, tone) is paired with an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US, foot-shock). After conditioning, the CS or the spatial context alone elicits a central state of fear expressed as reduced locomotor activity or total lack of movement (freezing).
4 automated cages (Coulbourn Instruments, Whitehall, USA)
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
The object recognition task is based on the natural tendency of rodents to explore a novel object / environment in comparison to a familiar one. This test allows evaluation of recognition memory to characterize potential memory defects.
Automated openfield arenas (Panlab, Barcelone, Spain) and different objects (marble, dice…) are required.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
This test is used to evaluate spatial reference memory in rodents. Mice are trained to escape from water by swimming to a submerged platform using only distal extra-maze cues.
2 rooms dedicated to water maze test and videotracking systems are used.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
These tests are used for evaluation of emotional learning and memory processes. In the active avoidance test, a conditioned stimulus (CS, light/tone) is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US, aversive foot-shock). The animals can avoid the foot-shock actively by leaving the compartment where they are in the interval-time between the CS onset and the US occurrence. In the passive task, mice receive a foot shock in a dark compartment. After conditioning, they can passively avoid, by staying in the light side where they are placed.
4 automated cages (Panlab, barcelona, Spain).
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
The scopolamine model is based on the fact that cholinergic system is altered in amnesic syndromes like Alzheimer's disease. Administration of scopolamine cause memory deficits in several tests.
Any equipment needed in tests used for evaluation of learning and memory.
10 mice per group are recommended for reliable data analysis.
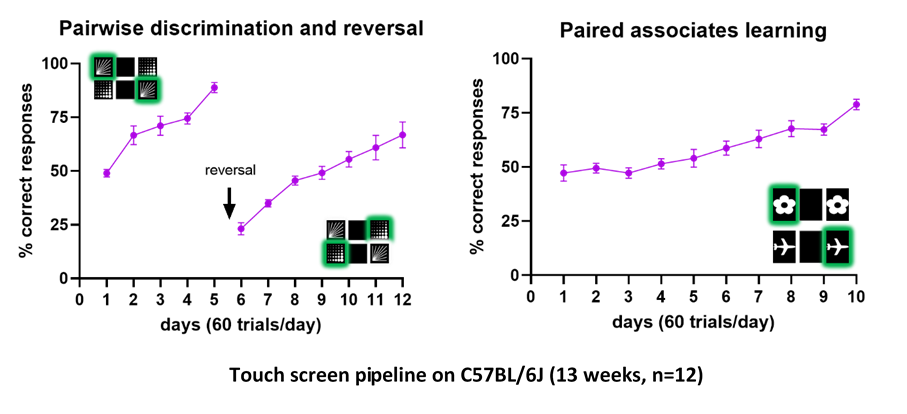
Touchscreen technology allows to explore cognitive deficits with a platform that is translatable across rodents, non-human primates and human subjects (Palmer et al., 2021) lending itself to a high degree of standardization and throughput.This methodology is low stress, using appetitive rather than aversive reinforcement.
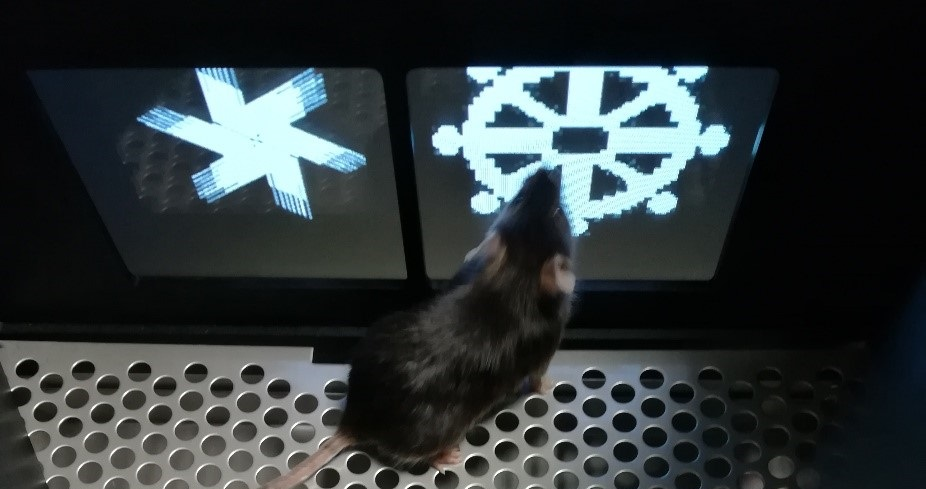

In addition to the traditional behavioral tests used to study cognitive skills, such as novel object recognition, Morris water maze, and fear conditioning, our team has implemented a touchscreen pipeline to assess visual discrimination, cognitive flexibility, and spatial learning.
After pre-training to learn to press an image that appears on the screen in order to obtain a reward of sweet water, the mice are tested in 3 different protocols.